Well Waterproofing
December 7, 2022
Wood Plank Effect
January 5, 2023How to Choose Waterproofing Materials for Walls and Foundations?
Selecting the right construction and waterproofing materials is not a simple task. The best approach is to consult a specialist, who can help assess which products will be most effective while considering financial constraints.
While price often correlates with quality, the most expensive solution is not always the most suitable.
Factors Influencing the Selection of Waterproofing Materials
Choosing waterproofing materials is more complex than simply following what a neighbor or family member recommends. Incorrectly selected materials may be ineffective, leading to costly repairs and replacement of the insulation.
Several factors must be considered to ensure proper waterproofing:
- Building type and usage – Different materials are required for indoor and outdoor applications, as exposure to UV radiation can degrade certain products.
- Application location – The selection depends on whether the waterproofing is applied to walls, foundations, or other structural elements.
- Climatic and groundwater conditions – Soil surveys provide essential information for choosing the right materials.
- Chemical exposure – Some soils and water contain aggressive compounds that may require additional protection.
- Sanitary requirements – Proper waterproofing ensures hygienic conditions and long-term cost savings.
Selecting Waterproofing Based on Risk Level
Water can threaten a building in multiple ways, including rain, snow, fog, and groundwater. Groundwater levels fluctuate throughout the year, making it critical to select a durable waterproofing system.
If uncertain, waterproofing against pressurized water is generally a safer choice than moisture-resistant insulation, as it provides higher protection levels.
Types and Uses of Waterproofing
In previous articles, we described different classifications of waterproofing materials, such as:
-
Installation method:
- Vertical waterproofing (external walls, foundation walls).
- Horizontal waterproofing (foundations, ceilings, and roofs).
-
Type of threat:
- Moisture-resistant (protection against humidity).
- Waterproof (protection against hydrostatic pressure).
-
Waterproofing intensity:
- Light – Protection against moisture penetration.
- Medium – Protection against direct, capillary, or seeping water.
- Heavy – Protection against pressurized water.
This article will focus on classifying waterproofing materials based on the materials they are made of:
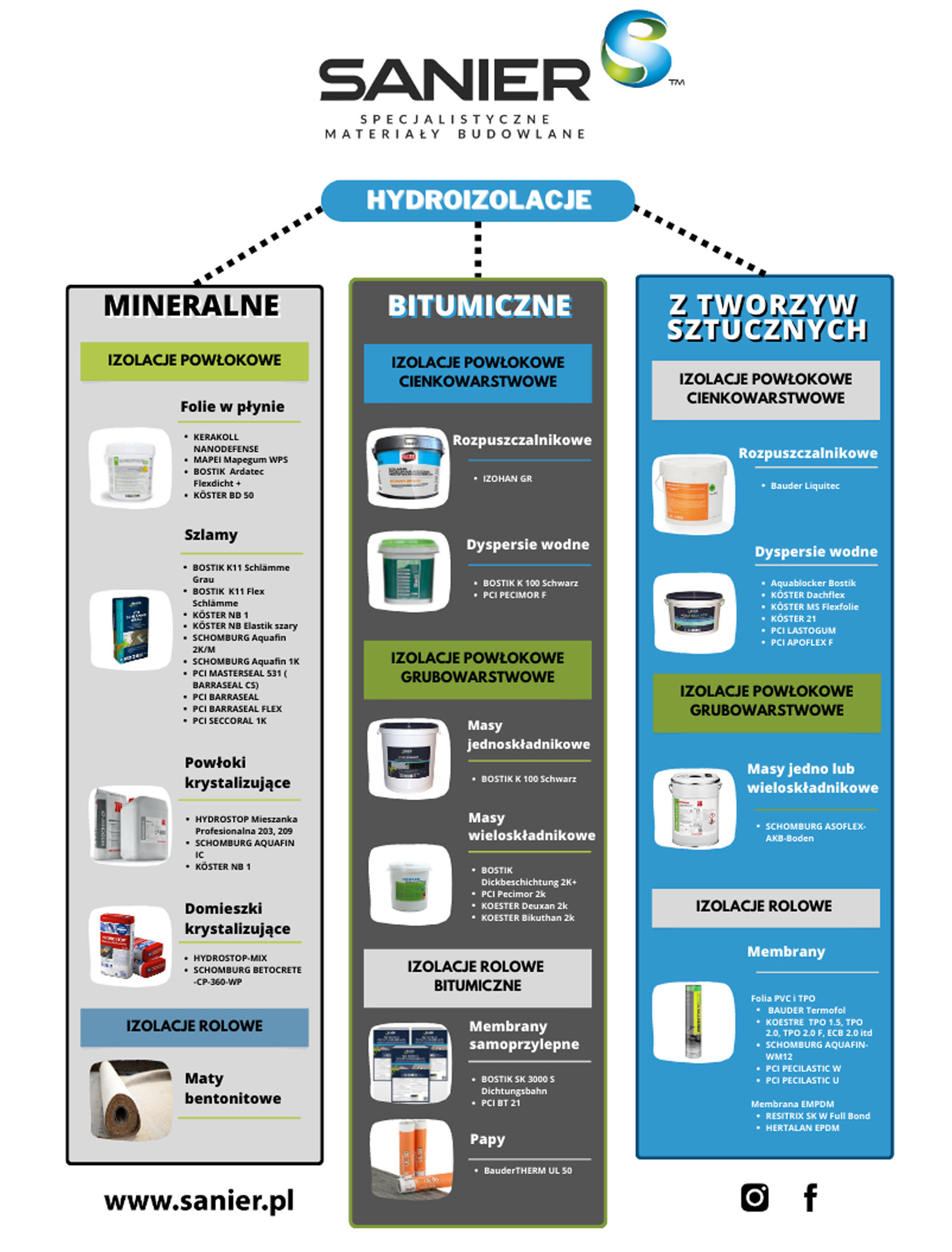
Single- or Two-Component Slurries
Single- or two-component slurries are flexible, cement-based coatings. Depending on the thickness and number of applied layers, they provide both waterproofing and moisture protection.
Features:
- Strong adhesion (even on damp surfaces)
- Elasticity
- Quick load-bearing capacity
- Crack-bridging
- Resistance to weak inorganic acids, alkaline solutions, municipal sewage, and UV radiation (not all products)
Applications:
- For mineral substrates (concrete, cement and anhydrite screeds, gypsum plasters, gypsum boards, ceramics) and asphalt substrates
- For moisture and waterproofing
- Positive and negative waterproofing
- On deformable and non-deformable surfaces as waterproofing for structures from the side opposite to water pressure
- Protection against moisture and groundwater (including pressurized water) in earth-covered structures, basements, underground garages, swimming pools, and potable water tanks
Bituminous Sheet Waterproofing
Bituminous sheet waterproofing includes self-adhesive bituminous membranes and roofing felt. Self-adhesive roofing felt can serve as the final waterproofing layer. The membrane consists of self-adhesive bitumen laminated with an HDPE film on the top, while self-adhesive roofing felt is reinforced with a fiberglass mesh.
Features:
- Easy and watertight joint sealing
- Fast application
- Immediate waterproofing
- Not vapor-permeable
Applications:
- Vertical and horizontal waterproofing
- Vapor barrier layer in balcony, terrace, flat roof, and green roof waterproofing systems
Sheet Waterproofing with Plastics
Features:
- Durable
- Easy to install
- Varied types, including flat sheets, membranes, and dimpled sheets made of polyethylene (PE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Applications:
- Moisture and vapor protection under roof coverings
- Moisture and waterproofing insulation for foundations







